Agentic AI is revolutionizing shipment delay prediction by utilizing real-time data from weather, traffic, and vehicle health to forecast and mitigate disruptions. These intelligent systems proactively identify risks and make autonomous adjustments to routes and schedules, minimizing delays and enhancing operational efficiency. By integrating agentic AI, companies can maintain reliable deliveries, increase customer satisfaction, and build more resilient, responsive logistics networks for sustained growth and success.
We’ve all been there — waiting eagerly for a package that’s caught in a mystery delay, stuck somewhere between “Out for Delivery” and “Processing.” For companies shipping across borders, these frustrating delays mean more than just inconvenience; they can cost time, money, and customer trust.
What if you could see delays coming and dodge them entirely? Enter AI agents, the game-changers of modern transport. These smart-systems leverage real-time data and predictive power to forecast disruptions, reroute around traffic or weather issues, and keep deliveries on track. With Agentic AI on your side, shipment delays don’t stand a chance. Let’s explore how AI Agents are transforming transport logistics into a seamless journey.
What is Shipment Delay Predication and Mitigation?
Shipment delay prediction and mitigation with AI agents refers to the use of advanced AI systems that analyze real-time data to forecast and address potential disruptions in the transport process. By leveraging machine learning, IoT sensor data, traffic patterns, weather forecasts, and historical shipment records, these AI agents identify risks such as congestion, poor weather, or vehicle issues that could lead to delays. For example, if an AI agent detects a severe weather warning along a delivery route, it can automatically reroute the shipment to avoid the storm or alert warehouse teams to prepare for a revised arrival time, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing costly delays. By anticipating disruptions, these AI systems optimize routes, adjust schedules, and enhance overall logistics efficiency, helping businesses improve operational performance and customer satisfaction.
A Brief Overview of Shipment Delay Prediction and Mitigation in Transport
Traditionally, shipment management has relied on manual processes where logistics teams assess potential delays based on factors like weather, traffic, and route conditions. These methods, while effective to an extent, can be slow, reactive, and prone to errors. As the volume of data grows, the demand for faster and more accurate decision-making has led to the integration of AI in shipment delay prediction and mitigation. AI agents can analyze vast amounts of real-time data from various sources, such as traffic reports, weather forecasts, vehicle performance, and historical trends, identifying potential disruptions with remarkable accuracy.
Autonomous AI agents are revolutionizing shipment management by automating key tasks, making the entire process more efficient and scalable. These agents use machine learning algorithms to predict delays, optimize routes, and suggest preventive actions. By analyzing structured and unstructured data, such as GPS data, weather patterns, and real-time traffic conditions, AI-driven systems help businesses predict potential disruptions in advance and take proactive steps to mitigate delays.
Traditional vs. Agentic AI Shipment Delay Prediction and Mitigation
| Aspect | Traditional Shipment Delay Mitigation | AI-Based Shipment Delay Mitigation |
| Monitoring | Reactive, based on after-the-fact inspections | Real-time monitoring from multiple data sources |
| Data Analysis | Limited, often using only historical data | Comprehensive, leveraging real-time and historical data |
| Responsiveness | Delayed, manual adjustments | Instant, automated responses |
| Human Intervention | High dependency on human oversight | Minimal human intervention; autonomous adjustments |
| Scalability | Challenging to scale and maintain consistency | Easily scalable with distributed AI agents |
| Predictive Maintenance | Reactive; based on fixed schedules | Proactive, using predictive insights for maintenance |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate due to high labor costs and inefficiencies | Cost-effective through optimized routes and reduced downtime |
Agentic AI Multi-Agent in Action
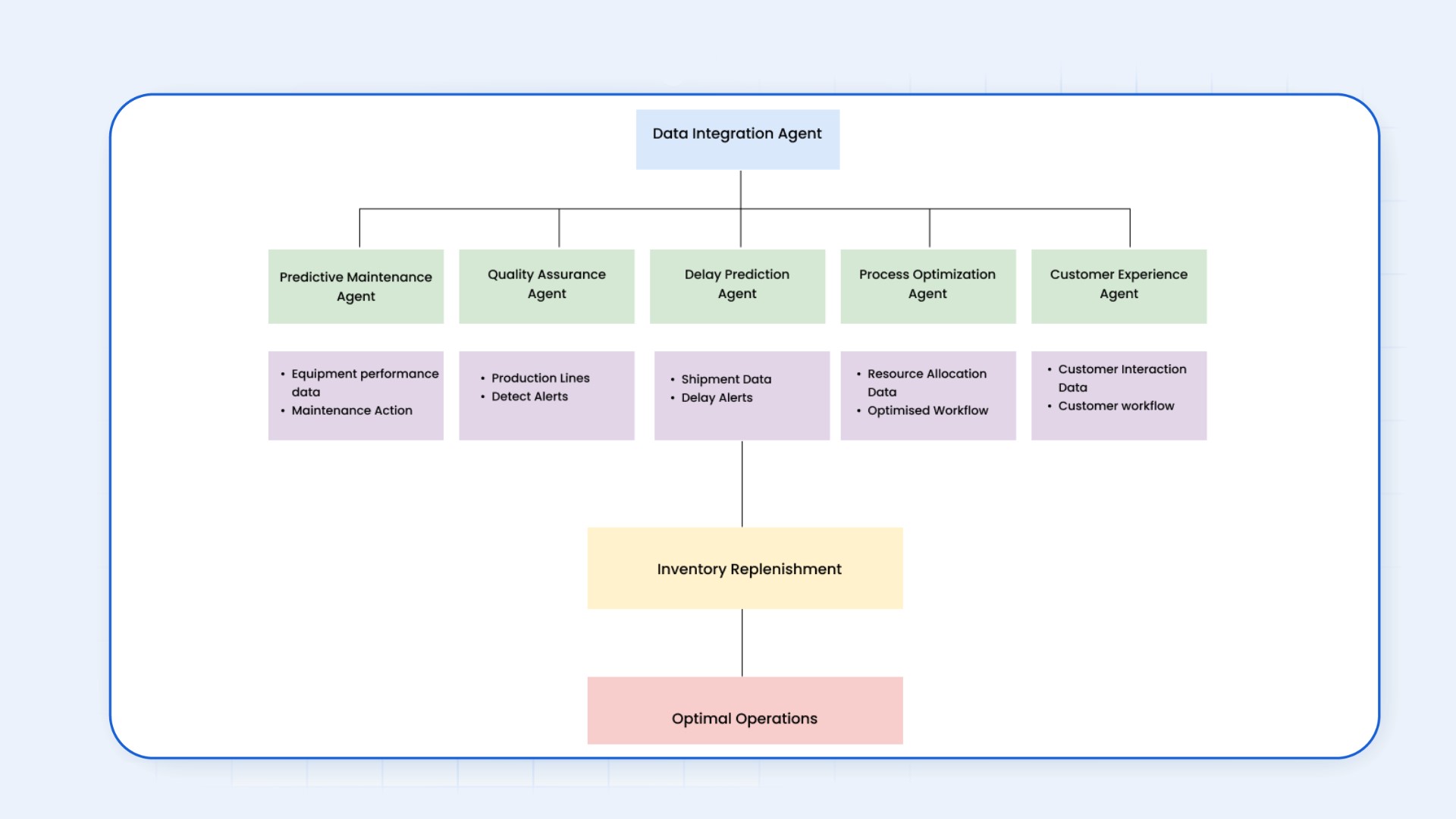
Agentic AI’s multi-agent system is designed to streamline and optimize complex operations across various industries, including manufacturing, telecom, and transport logistics. By leveraging the capabilities of specialized AI agents, the platform enhances efficiency, predictive capabilities, and decision-making through real-time data analysis and intelligent automation. Each agent plays a vital role in the system, collaborating with others to ensure smooth workflows, proactive issue resolution, and seamless coordination of tasks.
- Data Integration Agent: The Data Integration Agent unifies diverse data sources, including weather forecasts, traffic updates, shipping schedules, and GPS tracking, into a comprehensive dataset for seamless analysis.
- Delay Prediction Agent: The Delay Prediction Agent identifies potential shipment delays by analyzing integrated data for patterns such as adverse weather, congested routes, or operational bottlenecks.
- Inventory and Material Flow Agent: The Inventory and Material Flow Agent ensures material readiness by cross-checking inventory levels and providing contingency plans, such as sourcing from nearby warehouses.
- Process Optimization Agent: The Process Optimization Agent reorganizes workflows, adjusts schedules, and suggests optimal transport routes to minimize disruptions caused by delays.
- Customer Experience Agent: The Customer Experience Agent keeps stakeholders informed about potential delays and offers alternative solutions or revised delivery schedules to maintain satisfaction.
- Predictive Maintenance Agent: The Predictive Maintenance Agent monitors fleet health, identifying potential issues and scheduling preventive maintenance to minimize downtime.
- Quality Assurance Agent: The Quality Assurance Agent upholds delivery standards by verifying shipment handling, ensuring no damage, and maintaining customer trust.
Use Cases of Shipment Delay Prediction and Mitigation
- Route Optimization for Cross-Border Deliveries: By analyzing potential bottlenecks in real-time, such as customs delays and high-traffic areas, intelligent systems select the fastest and most efficient routes for cross-border shipments. This proactive approach helps businesses avoid costly delays and provide more accurate delivery timelines.
- Dynamic Weather Analysis for Coastal Shipping: Live weather data integration helps anticipate adverse conditions on coastal and maritime routes. With this information, businesses can make informed decisions about rerouting shipments or delaying departures, ensuring safer, more timely deliveries.
- Vehicle Health Monitoring for Fleet Reliability: IoT sensors monitor key vehicle metrics like fuel efficiency, engine temperature, and tire wear. By predicting mechanical issues before they occur, businesses can prevent unexpected breakdowns, reducing the chances of shipment delays.
- Traffic Prediction and Real-Time Rerouting: Continuous tracking of traffic conditions and potential roadblocks allows for dynamic rerouting of vehicles. This ensures deliveries remain on time even during peak traffic hours or sudden road closures.
- Inventory Reallocation Based on Predicted Delays: Intelligent systems can predict delays and, in response, reassign inventory to nearby distribution centers or adjust shipment routes. This proactive strategy helps avoid backorders and minimizes the impact of delays on customer
Operational Benefits of Shipment Delay Prediction and Mitigation
- Increased Efficiency: By predicting and mitigating delays, companies can boost efficiency across their logistics networks. Autonomous adjustments help minimize idle times, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure better allocation of resources, leading to smoother operations.
- Enhanced Predictive Accuracy: Delay prediction systems can achieve an accuracy rate of 85% or higher, providing businesses with the insights needed to make informed decisions about rerouting or rescheduling shipments. This allows companies to anticipate potential disruptions and implement alternative measures immediately.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Effective delay management reduces the need for emergency shipping fees, overtime labor, and costly last-minute adjustments. By avoiding delays, businesses can lower warehousing costs and streamline logistical operations, ultimately reducing overhead expenses.
- Higher Customer Satisfaction: Minimizing delays improves on-time delivery rates, which boosts customer satisfaction and fosters loyalty. Reliable service is a key driver of customer retention, as clients are more likely to remain loyal to companies that consistently meet delivery expectations.
With predictive systems handling a majority of shipment tracking and delay mitigation tasks, businesses can expect a 30% productivity boost and a 25% reduction in delay-related costs by 2025. These improvements contribute significantly to ROI, allowing companies to optimize resource usage and enhance profitability.
Technologies Transforming Shipment Delay Prediction and Mitigation
- IoT Sensors: These provide real-time updates on vehicle status, traffic, and environmental conditions, feeding critical data into AI systems for rapid analysis.
- Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics: Advanced machine learning algorithms help AI agents predict delays based on historical data, allowing them to spot trends and proactively adjust shipments.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of shipments and routes enable AI agents to simulate different scenarios, optimizing routes and timelines based on predictive data.
- Edge Computing: With edge computing, data processing happens locally, allowing for faster decision-making in real-time and reducing the dependence on centralized systems.
- 5G Connectivity: High-speed data transfer supports the instantaneous exchange of information between AI agents, vehicles, and logistics systems, enhancing real-time responsiveness.
- Autonomous Multi-Agent System: Multiple AI agents work collaboratively, sharing data and decisions, to efficiently optimize transport networks and make coordinated adjustments to prevent delays.
Future Trends in Shipment Delay Prediction and Mitigation
- Self-Optimizing Logistics Networks: Logistics systems will autonomously adjust routes, schedules, and resources to optimize delivery timelines, minimizing the need for manual oversight and ensuring more efficient operations across the network.
- Enhanced Real-Time Collaboration: Increased connectivity among vehicles, warehouses, and agents will create a synchronized transport network, improving coordination and boosting overall efficiency by enabling real-time updates and decision-making.
- Refined Predictive Accuracy: As predictive models evolve, they will offer even greater accuracy in forecasting delays, learning from past events and continuously refining their predictions to improve decision-making and minimize disruptions.
- Personalized Delivery Schedules: Systems will adapt delivery times and routes to align with customer preferences, enhancing satisfaction and fostering loyalty by offering a more tailored, flexible service.
- Sustainable Logistics Operations: By prioritizing fuel-efficient routes and minimizing unnecessary mileage, logistics networks will reduce their carbon footprint, supporting sustainability goals and contributing to more eco-friendly operations across the industry.
Conclusion: AI Agents for Shipment Delay Prediction
AI agents are transforming shipment delay prediction and mitigation in the transport sector, bringing unprecedented efficiency and reliability. By analyzing real-time data and making proactive adjustments, these systems ensure timely delivery, improve customer satisfaction and reduce operational costs. The future of logistics lies in autonomous, self-optimizing networks that can respond instantly to any disruption, making transport a more dependable and resilient part of the global economy.